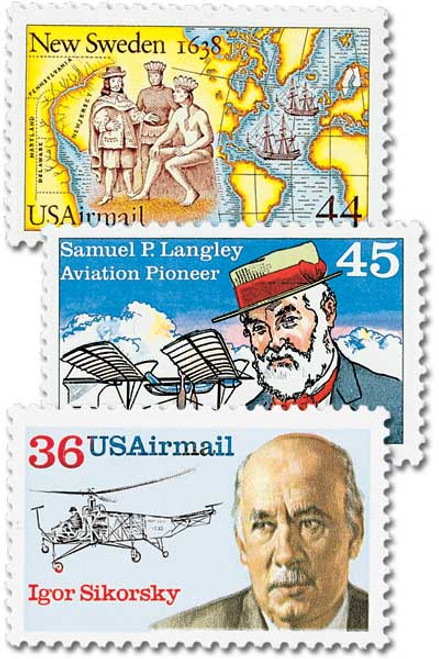
# C118 - 1988 45c Samuel P. Langley Airmail
Â
1988 45¢ Samuel Langley
First City:Â San Diego, California
Quantity Issued: Â 201,150,000
Printed by: Bureau of Engraving and Printing
Printing Method: Lithographed, engraved
Perforation:Â 11
Birth Of Samuel P. Langley
Langley attended the Boston Latin School and English High School of Boston before serving as an assistant at the Harvard College Observatory. After that, he worked as a professor of mathematics at the US Naval Academy.  While there, he also worked on restoring the school’s small observatory.
In 1867, Langley moved to the Western University of Pennsylvania and became director of the Allegheny Observatory, as well as an astronomy professor. When he arrived, the observatory was in need of repair and new equipment. He raised money for the renovations by distributing standard times to the railroads.

Trains ran on a strict schedule. Engineers and switch operators used their watches to keep track of time, but there was no standard to set the watches to. Langley used astronomical observations to obtain a precise time and then sent it by telegraph to railroads throughout the US. This system was the basis for Standard Time Zones.

Langley used the money from the railroads to fund research into the sun. He produced drawings of solar activity that were published in the US and Europe. He also invented the bolometer, which measures infrared radiation. This instrument was used by scientist Svante Arrhenius to demonstrate the greenhouse effect for the first time.
In addition to his work at the observatory, Langley experimented extensively with heavier-than-air aircraft. By 1887, he was living in and employed at the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, DC. He began his experiments with rubber band powered models. His work advanced to steam engine powered flying machines that he called “Aerodromes†(meaning air runner in Greek). He built a spinning table, which functioned like a wind tunnel, to test his early models.

After many failed flights, Langley achieved success on May 6, 1896. That day he launched his Aerodrome No. 5 using a catapult attached to the top of a houseboat. The unpiloted model weighed less than 25 pounds and had a pair of wings at each end of the plane with propellers in the middle. After a 3,300-foot-long flight (ten times longer than any previous heavier-than-air machine), the Aerodrome landed safely in the Potomac River as planned, because there was no landing gear.

The War Department took notice of Langley’s aerodromes and gave him a grant of $50,000 to develop an airplane capable of carrying a pilot. He began this work in 1898 with Charles Manly, who was both an engineer and test pilot. In 1903, they launched their craft from the catapult. The plane had no landing gear, so it had to land in the water and be repaired after each flight. Two flights ended in crashes, and though Manly was not hurt, Langley gave up his attempts at manned flight. In 1914, Glenn Curtiss continued Langley’s work and developed an aerodrome that flew a few hundred feet.
Samuel Langley paved the way for the further development in the fields of aviation and solar radiation. He died on February 27, 1906, in Aiken, South Carolina. Several things have been named in his honor, including air and sea craft, a unit of solar radiation, and the Smithsonian’s Langley Gold Medal. He’s also the namesake of the NASA Langley Research Center (NASA’s oldest field center) as well as Langley Air Force Base.
Â
Â
1988 45¢ Samuel Langley
First City:Â San Diego, California
Quantity Issued: Â 201,150,000
Printed by: Bureau of Engraving and Printing
Printing Method: Lithographed, engraved
Perforation:Â 11
Birth Of Samuel P. Langley
Langley attended the Boston Latin School and English High School of Boston before serving as an assistant at the Harvard College Observatory. After that, he worked as a professor of mathematics at the US Naval Academy.  While there, he also worked on restoring the school’s small observatory.
In 1867, Langley moved to the Western University of Pennsylvania and became director of the Allegheny Observatory, as well as an astronomy professor. When he arrived, the observatory was in need of repair and new equipment. He raised money for the renovations by distributing standard times to the railroads.

Trains ran on a strict schedule. Engineers and switch operators used their watches to keep track of time, but there was no standard to set the watches to. Langley used astronomical observations to obtain a precise time and then sent it by telegraph to railroads throughout the US. This system was the basis for Standard Time Zones.

Langley used the money from the railroads to fund research into the sun. He produced drawings of solar activity that were published in the US and Europe. He also invented the bolometer, which measures infrared radiation. This instrument was used by scientist Svante Arrhenius to demonstrate the greenhouse effect for the first time.
In addition to his work at the observatory, Langley experimented extensively with heavier-than-air aircraft. By 1887, he was living in and employed at the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, DC. He began his experiments with rubber band powered models. His work advanced to steam engine powered flying machines that he called “Aerodromes†(meaning air runner in Greek). He built a spinning table, which functioned like a wind tunnel, to test his early models.

After many failed flights, Langley achieved success on May 6, 1896. That day he launched his Aerodrome No. 5 using a catapult attached to the top of a houseboat. The unpiloted model weighed less than 25 pounds and had a pair of wings at each end of the plane with propellers in the middle. After a 3,300-foot-long flight (ten times longer than any previous heavier-than-air machine), the Aerodrome landed safely in the Potomac River as planned, because there was no landing gear.

The War Department took notice of Langley’s aerodromes and gave him a grant of $50,000 to develop an airplane capable of carrying a pilot. He began this work in 1898 with Charles Manly, who was both an engineer and test pilot. In 1903, they launched their craft from the catapult. The plane had no landing gear, so it had to land in the water and be repaired after each flight. Two flights ended in crashes, and though Manly was not hurt, Langley gave up his attempts at manned flight. In 1914, Glenn Curtiss continued Langley’s work and developed an aerodrome that flew a few hundred feet.
Samuel Langley paved the way for the further development in the fields of aviation and solar radiation. He died on February 27, 1906, in Aiken, South Carolina. Several things have been named in his honor, including air and sea craft, a unit of solar radiation, and the Smithsonian’s Langley Gold Medal. He’s also the namesake of the NASA Langley Research Center (NASA’s oldest field center) as well as Langley Air Force Base.
Â